Digital Marketing Trends: 2022 & Beyond
Last week, we had the wonderful Mike Eastwood, founder of Webalite and proudly self-titled ‘Marketing Geek’, present to GMA on what was in store for 2022 and beyond in the way of digital marketing trends. In this extensive - but concise and easy to digest - blog, Mike further summaries the stuff you really need to know.
We’re going to travel into the future and unpack some of the buzzwords you’ve heard from other geeks. We’ll come back briefly and look at some things you can do to prepare, then look at the near future with some of the tech that will impact you.
How does a combustion engine work?
This looks like a strange place to start but it’s relevant because most of our clients can not explain how a combustion engine works, nor do they need to. They’re happy to jump in their car and drive home early at the end of the day.
The Metaverse
When Facebook renamed their parent company meta, the media went into a frenzy talking about the Metaverse. So what is the metaverse? Think about it as a 3D virtual world. They say there will be interconnected 3D worlds but I think that’s unlikely for a number of reasons. Currently, social media networks put a huge amount of effort and resources into keeping you within their walls. They don’t want you wandering off.
The 3D world will be accessible on standard screens but is really designed to be viewed with 3D headsets (more on that below). Accessing the internet will fundamentally change, the ways in which we interact with other people will be affected, and then things we’d normally do online e.g. games, social media, news and work will change too.
You’ll notice in the picture that the Avatars (representations of us) have no legs, that’s because the majority of controllers (that move us around the metaverse) don’t know where our feet are – our hands have controllers, or cameras that can see our hands; our eyes have goggles or full headsets so it’s easy to map where we’re looking, but our feet are generally nowhere to be seen.
This video show Microsoft and Facebook’s visions of the Metaverse.
[Not] Real Estate
Because the Metaverse is essentially a 3D world, designers, architects and speculators have leapt at the opportunity to create ‘[not] real estate’ in the Metaverse. Speculators are spending millions of dollars on “property” in the virtual world.
Virtual worlds are representing traditional roads to shops in malls, right up to luxury venues. They seem to be stuck in a bricks and mortar mindset with roads that don’t need to exist because we won’t need to drive anywhere.
The first Fashion Week in the Metaverse
Luxury brands quickly made the leap into selling virtual clothes so your avatar can make a statement. And, like the real world, the luxury brands come at an eye watering cost for digital clothes.
Decentaland , a virtual world in the Metaverse, is hosting Fashion Week from 24-27 March 2022. Designers will be exhibiting some inspiring work (and some work that would look normal in the real world, not sure why you’d bother). You’ll be able to buy designer clothing for your avatar, and NFTs, from top brands like D&G, Balenciaga, Gucci and more.
Remember, it’s free if you are the product
The internet quickly became a gold rush for advertisers and developers. By offering free products businesses were able to leverage your visits by selling advertisements, then they realised your personal data (demographics, behaviours and even conversations) could be mined and sold to advertisers for even more money.
Privacy laws and initiatives to curtail some of the worst behaviour have started to turn the tide toward respecting peoples’ privacy, so hopefully this will help shape the Metaverse to be a more secure and private world.
While the Metaverse may not be relevant to your marketing now, you will probably be able to advertise to your customers in the future. And you will have the opportunity to create a brand experience in the virtual world for real people.
Virtual Reality
Stereoscopic headsets create a visual and audible immersion in a 3-dimensional virtual world. The technology has been around for a while (do you remember the Viewmaster when you were a kid?) but the user interfaces were rudimentary. They have only recently progressed enough that you can go into a 3D space without wanting to throw up. While the image quality and screen rate have improved significantly, the metaverse you can view now is still more like an old school video game than a visually convincing world. We are currently in a transitional phase and it won’t be long before you can’t tell the difference. Think of the difference between the early computer-generated special effects in movies, compared to now.
AR – Augmented Reality
Augmented reality blends the real world with a computer overlay. We’ll eventually be able to hold up our phone, or look through glasses, and see a digital overlay of the real world with information that is relevant to us. In this example of Apple’s new headquarters (pic above), the tablets are mapping the details over the model in front of the people. While this tech is currently available, it’s not yet ready for the real world we live in – the computing power to process the real world is too immense for current devices or efficient cloud processes (basically the Augmented Reality only works in controlled environments with limited options for overlays). Real world mapping, with camera images and geospatial data will be here soon and most probably in your car.
Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 is a product you can buy now, the combination of glasses, with projected images over the real world, create an amazing opportunity for work environments and games (if you can afford the kit).
The marketing opportunities using AR are still yet to be fully realised, but the bridge is QR Codes and other codes than can be easily scanned and mapped by mobile devices.
But, here’s where we are now - on Zoom
Video conferencing experienced exponential growth during the pandemic. Instead of zooming into work we would Zoom to work. The rapid adoption was great for many of us because we could work from home. This change in the workforce – for white collar workers – was one of the most significant technological changes, for most people, since the personal computer.
Work from home anywhere
Once the workforce realised they no longer needed to commute they then wondered what if I work from another place? Airbnb have seen a 68% increase in long-term stays. I invite you to listen to a podcast where Brian Chesky, the CEO of Airbnb is talking to Nilay Patel about the future of work – it’s packed with interesting insights.
“68% increase in long term stays”
Now your loyal three-time-a-week shopper is in a different city. When they used to be able to buy your product, from a store, on their commute home you had a regular purchase.
Now your customers may not be able to get your product where they are staying – can they get your product delivered online? Have you created enough connection and brand loyalty, so they want to make the effort to buy your product online? Or will they switch to your competitor’s product and switch again if they return home?
Mobile First
During 2016 mobile phone traffic on the internet surpassed desktop traffic and it’s only going to keep increasing as more of the world get online..
Your website must be mobile friendly. Not only will your website visitors leave your website if it’s slow, or a bad experience, but Google will demote your page in the search results if your website has come up short.
Homework for you – check your website on Google’s Mobile Friendly Test
Homework for experts – set up Google Search Console for your website so you know when Google finds any issues on your website
Core Web Vitals
Every geek like me is nervous when pointing Google’s Core Web Vitals audit at a website. There’s a constant balance of creating an amazing experience for the visitor, while keeping the site optimised for the lowest common denominator (an old smartphone with a slow connection). You may decide to compromise the size of the page to load more high-quality images, but you should always optimise for speed and usability.
LCP - Largest Contentful paint
How fast can you get content on screen so the visitor can start to browse? The first impression is important and a study by Amazon, in 2006, found that every 100ms delay in page load speed cost them 1% of sales through abandonment (about $107M at the time). Your developer may need to prioritise some content while the rest of the page is still loading so a visitor has a responsive experience. The old fashioned comparison is when we used to turn on our computer before we made coffee because it took so long to boot.
FID – First Input Delay
How long before you can interact with the website? This is important because we’re getting more impatient. If we can’t do anything while we wait for stuff to load is really frustrating. The old fashioned comparison would be phoning your bank and waiting for 14 minutes on hold before your call is answered (oh, that still happens).
CLS – Cumulative Layout Shift
How much does stuff move around the screen while it loads? Most of us have clicked on something – and ended up in the wrong place – because the content was jumping around the screen because it was still loading. This is one of the easier issues to fix.
Homework test your site on Google’s Page Speed Insights
Beware – it’s disheartening the first time your run the test because it’s very difficult to get a “good” score.
Voice Search
Why do I have to worry about page speed? Won’t everyone be searching be asking Siri? While voice search has increased dramatically (X5 increase), most of us will still have a huge amount of screen time. And, if you’ve used any voice searches you’ll realise why the number of queries is so high – you often have to ask a few times before your voice assistant does what you want.
Position Zero
Voice search uses Artificial Intelligence to analyse millions of web pages to return useful replies to your query. Also, Google can return answers to your question on the Search Page, at the top, known as Position Zero.
As you can see in the picture, Google has explained what Position Zero is above the first search result. Often that’s enough to answer a searchers question, and there is no click to your website. However, by creating good content you will naturally attract visitors to your website and Google will help.
ZMOT – Zero Moment of Truth
In the olden days, when sales people had more power to influence the purchase process, the first moment of truth was often when people interacted with a product in the store for the first time. The first moment was real and tangible and brands invested in the experience of purchasing a product with flagship stores and customer experience.
The second moment of truth is when a product delivers on the brand promise, this is typically when the product is used for the first time.
The third moment of truth is when a consumer gives feedback – positive or negative – to the company, or a friend (referral).
Proctor & Gamble’s Chairman, Alan George "A. G." Lafley, introduced the Moments of Truth concept in 2005. Then, in 2011 Google introduced the Zero Moment of Truth because the internet has fundamentally changed the experience from a Customer’s Journey to a Buyer’s Journey.
The Zero Moment is online, often before the consumer has seen or interacted with the product.
“81% of retail shoppers conduct online research before buying.”
Think of your Buyer’s Journey, what are your touchpoints? What is your online experience like? How does a visitor feel when visiting your website for the first time?
Learn more about the Zero Moments of Truth at Think with Google.
7/11/4
For businesses with a longer sales process Google’s research team found that buyers, on average, will spend seven hours, with eleven touchpoints, across 4 channels.
7 hours – this could be reading blogs, watching videos, talking to a sales person
11 touchpoints – this includes your website, advertising, social media, review sites, etc.
4 channels – this includes your website, your store (if you have one), third party websites, traditional media e.g. magazine articles.
So, as you can see the more you extend your brand across channels where your potential customers are the more likely you are to succeed.
Omnichannel Marketing
We know everyone is using the internet to do product research before they buy, so how do we connect with them? Omnichannel marketing has replaced traditional multichannel marketing. Traditional multichannel marketing would hope a billboard planted a seed that helped you recognised a brand in another channel, that would attract you and persuade you to engage. I say hope because traditional media wasn’t as easy to measure as digital marketing.
Omnichannel marketing leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI) to connect different channels to the consumer. The internet has allowed advertisers and marketers to gather personal information that allows systems to connect your visits across multiple channels. You will have seen it when you do a search on Google and suddenly you get ads, relevant from your search, following you around the internet.
While this is powerful for marketing and advertising it’s at the expense of your privacy. Do you really want someone to see your screen advertising aka. something you’re not comfortable sharing, just because you clicked through to a website?
Martech
Short for marketing technology, MarTech is how all these channels, networks and software connect to give savvy marketers the edge. The evolution of the internet has meant that customer data no longer exists in silo’s accessed by a few people with statistical degrees. AI is now helping all of us leverage data to provide better experiences for our customers. For example, composing an email that’s hyper-relevant to the recipient.
And, on the flip side, the technology has been abused by businesses and political organisations to our detriment.
In 2008, Scott Brinker AKA Chief Martech started blogging about Marketing Technology and by 2011, he had mapped the landscape in his infographic. The famous image showed 150 Marketing Technology Companies, by 2020 the number had ballooned to over 8,000 Martech companies.
Digital Natives – the shift in demographics
Digital Natives grew up with the internet. They’ve always been connected to the world via a screen and often can’t imagine a world without the internet.
Digital natives include Gen Z and Millennials. You’ve probably heard these terms – often unfavourably – so here’s each generation and the years they were born:
Gen Z were born between 1997 and 2012
Millennials were born between 1981 and 1996
Gen X were born between 1965 and 1980
Boomers were born between 1947 and 1964
Silent Gen were born between 1929 and 1946
Greatest Gen were born 1916 and 1928
As you can see by the chart below if you’re not addressing the shift in spending power – as Digital Natives get older – your market is dying, literally.
5G – 5th Generation
For years, the speed and volume of data being transmitted over the mobile phone network has been increasing – from impossible (1G), to utterly frustrating (2G), to annoyingly slow (3G) and now most of us in cities use 4G with comparative ease. 5G is next level – we will be able to download content at dizzying speeds. While the volume of data consumed will increase (think how much more data the metaverse will consume compared to now) 5G should be able to cope (for a while).
The downside of 5G is that we will need many more cell-sites to get the same coverage we do for 4G. 5G is based on a shorter wavelength. The signal doesn’t travel as far, so we need more repeaters, more signal towers, and generally more infrastructure. The roll out will take time and we should only expect it in urban centres.
IOT – The Internet of Things
We’ll also have more devices generating data. You thought your home Wi-Fi was crowded with everyone having multiple devices (phone, tablet, computer), soon all your appliances will be on the internet too.
Your TV, your music, your lighting, your heat pump, your doors and windows, your home security, everything. Smart homes will have all your appliances connected to the internet – ordering consumables when they need them, heating your home before you get there, customising the lighting for the people at home.
The rural sector is way ahead of the cities with this because our farmers do not give people-centred levels of personal liberty and privacy to their crops and livestock. High tech agriculture allows farm managers to work from the kitchen table. Farmers are using soil sensors to control watering and inputs, gate monitors to control stock movement, milking sheds are mechanised and automated, feed stalls provide food and medicines targeted to an individual animal's needs.
The Blockchain
We don’t need to know how a blockchain works, we only need to know what it does. At its most simple a blockchain is a digital receipt. It provides us with a way to verify that an exchange has occurred on the internet.
Blockchain chain technology allows strangers to do business securely in a zero trust environment. Historically we have all operated in environments of trust. Every time we interact with one another we engage in acts of trust. We’re so hard-wired for trust that we “just know” when we can trust someone or not. The challenge of the internet and digital transactions is that we can’t tell what to trust, who to trust, or when to trust them. All of our best methods for establishing trust have been removed. That’s where the blockchain steps in.
The blockchain has been designed to generate authenticity instead. It bases its authenticity on a unique set of facts. Those facts generate an object that is completely unique, and can be easily verified by all parties. Think of it as a really complicated jigsaw puzzle. If any of the pieces are missing, or changed in any way, you won’t be able to reconstruct the puzzle.
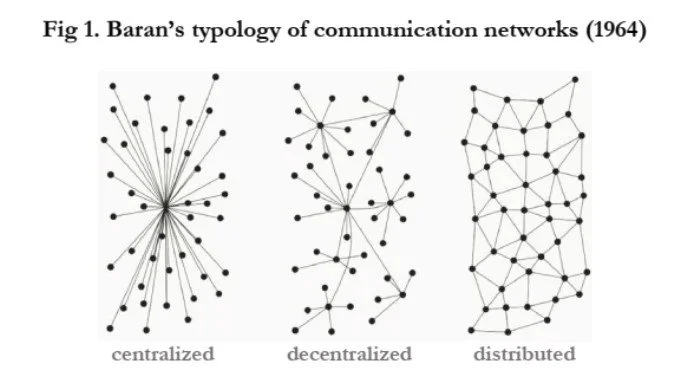
Decentralised
Most networks we use now are essentially decentralised networks where the data is stored with an organisation. For example your Gmail is replicated across several servers, so the infrastructure is decentralised, but your data is only held on Google’s infrastructure so it’s considered centralised.
Technologies based on blockchain authentication, think of cryptocurrencies, rely on a decentralised network where the data is replicated onto multiple computers, across multiple networks. This creates stability and safety for the data and reduces weaknesses inherent in any single network. Many, many parts of the network can fail and the system remains intact.
This diagram, from the Sixties, illustrates the different networks:
NFT – Non Fungible Token
Another buzzword in the media, blown up by speculators, is NFTs or Non-Fungible Token. The NFT is essentially the original digital artwork (visual or audible) stored on the blockchain to prove ownership.
Yes, in the example of digital artwork it’s the same set of pixels. Yes you can copy them, share them, distribute them. But, if you tried to sell those pixels then the blockchain will prove if they are in fact the original work.
The “overnight” success of people in the Cryptocurrency space has fueled the boom in NFTs because you purchase NFTs with cryptocurrency. Digital artwork is being sold at unprecedented prices.
This example of Beeple sold at auction for $69 million USD. The artist Mike Winkelmann produced a piece of digital art every day for 5,000 days. He’d built up a huge online following even though the most anyone had paid for a physical item was $100 USD.
Crypto Currency
As comedian John Oliver put it, in his episode on Cryptocurrencies:
“It’s everything you don’t understand about money combined with everything you don’t understand about computers…”.
But seriously, cryptocurrency is the way of the future for money. It’s decentralised, it works in countries without banking infrastructure, you access it from your smartphones. It’s global and it’s getting cheaper and cheaper to use.
Admittedly cryptocurrency has it’s issues:
Energy consumption is an ongoing issue and new cryptocurrencies are only just starting to address the issue.
Countries are banning cryptocurrencies because they are worried that it will be unregulated, un-policeable and will make it harder to collect tax revenue.
Current cryptocurrencies are still too volatile to trade with – if a currency can move 40% in a week then it’s too unstable for day to day commerce.
Cryptocurrency exchanges are still too slow to be used for day to day commerce (Visa currently processes 65,000 transactions per second. Compare that to Ethereum at 16 transactions per second). The speed of transactions is being addressed by both new and old cryptocurrencies.
Decentralised Finance, or Defi is the future of money. There are 10,397 different Cryptocurrencies today (18 February 2022) and there will be new ones added all the time. But, there will be a huge drop in the number of currencies as chains collapse, criminal schemes are exposed and legitimate companies fail to adapt to an ever shifting landscape.
Web 3.0
Web 3.0 has a different definition depending on who you ask. The fundamental idea is that everyone has access to everything and everything is open. It’s about openness and transparency. The interpretations of what openness and transparency mean for your environment can range from flossy utopianism to post-apocalyptic survivalism.
These are some of the most important elements for web 3.0.
No secrets ( open source code ↔ your password was cracked)
No favours ( everyone welcome ↔ no one gets in )
No assumptions ( no authentication needed ↔ blockchain everywhere )
It will be available in 3D flavours
And, we also know that everything I said about the future of Digital Marketing could be completely wrong and everything I’ve written will live – in perpetuity – on the internet for everyone to see.